What does AQL mean?
When using 3rd party QC, AQL standards are one important factor to understand how to select random samples for product inspections.
The most commonly used standard for product inspections is standard ISO 2859-1 (ANSI/ASQC Z1.4-2003). It uses the concept of AQL, or Acceptable Quality Limit.
The definition of the AQL (Acceptable Quality Limit) is “the maximum defective percent (or the maximum number of defects per hundred units) that, for purpose of sampling inspection, can be considered satisfactory as a process average”.
A sampling size, based on the AQL tables, will be selected and then inspected for defects.
Defects are broken into 3 categories: Minor, Major and Critical. While these can vary from client to client, the typical definitions are as follow:
- A Minor defect is a discrepancy from the standards, but one that is not likely to affect the usability of an object.
- A Major defect is one that is likely to create failure of the unit for its intended purpose.
- A Critical defect is one that is deemed to be hazardous or unsafe.
According to the number of defects found for each type and according to the number of defects allowed (figures given by the AQL sampling tables), your QC company can advise you to accept or to reject your shipment.
How to use the AQL Tables?
Client can set their Acceptable Quality Tolerance but the AQL tables will help to determine the sampling size we will need to inspect according to your ordered quantity and your level of severity. You can choose Levels I, II or III, with Level III being the most stringent testing and Level I being the least. The standard level, the one used by default and by 98% of the people is the Level II. This is up to the client, but it is the recommended level.
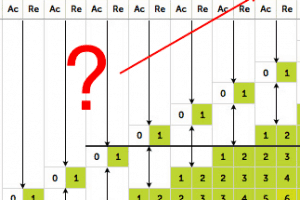
In order to find the necessary sampling size to be inspected, you must first look at the first chart and find on the left side the range of items being produced in total. For example, if you are producing 8000 items, at Level II you have the letter L, which in the second table corresponds to a sample size of 200.
On the top of the second chart are the defect levels, ranging from 0 to 6.5 (we cut the higher values out of the chart, because they are not relevant for buyers of consumer goods).
You can choose which level to apply for your type of defect: critical, major and minor. Usually most importers will choose standard defect levels which are 0/2.5/4.0, AQL 2.5, but one can choose 0/1.5/2.5 if he wishes.
Using the standard 0/2.5/4 defect levels and a sample size of 200, we see that if you have more than 0 critical defects, 10 major defects or 14 minor defects, you should reject your shipment.
Of course the decision about what to do after your received the inspection results belongs to you. Most importers will wish to discuss all inspection findings with their vendor/manufacturer in order to improve whatever possible. In case the inspection results are very close to AQL limits, it is important that you double check if the level of found defects is acceptable to you or not.




i already read a definition and explaination,
qty of sampling is base on sampling size,is it correct?
then,i still not get it about minor and major defect.
your statement is 10major defect and 14minor defect.
but on schedule that u provide,10 and 14 is AC it will be accept right.
but it call defect?
i need detail about this because just now i set up my department.
hopefully you can help me.
@ Ah Meng: Thank you for your message and questions. To define the sampling size (the number of pieces to be inspected) you need to know the order quantity and to determine your level of Acceptable Quality (level I, II or III)
Major, Minor defects, if 10 and 14 are within the column AC it means that you are willing to accept 10 major defects and 14 minor defects. If the QC finds 11 major defects or 15 minor defects, he will consider the quality of the goods as unacceptable. For a deeper understanding, check out the following articles and feel free to come back to us if any questions: http://www.asiaqualityfocus.com/blog/?s=AQL+table&submit=Search
01. what is 2.5/4.0 & from where is came ? what is the calculation behind it ?
02. if lot size is 3201-10000 Pcs sample size will be 200 in AQL 2.5/4.0 now the question is how sample size is determined 200 Pcs ? what is the calculation behind it ?
03. how AQL Level are determined ?
@Syed Munna: thank you for your questions. The AQL tables have been developed by the USA army. To learn more about where it comes from, we invite you to read this complementary article http://www.asiaqualityfocus.com/blog/aql-table-definition-and-role/. Feel free to come back to us if any question!
[…] we have introduced AQL in general and discussed the standard inspection levels. But how do inspection companies do other testing […]
[…] AQL (cosmetic of your sampling size) […]
Hi. Thank you for the informative outline. From having read various articles explaining AQL, it appears to be a simple % value that the customer is willing to accept. eg. 2.5 is an indication that the customer is willing to accept 2.5% rejects in his batch. If this is the case, what do the AQL values above 100 mean? Have I misunderstood something? Please explain what AQL levels above 100 indicate
ASQ Z1.4 section 3.1: the extent of nonconformance of product shall be expressed either in terms of “percent nonconforming” or in terms of “nonconformities per 100 units”. Section 3.2 and 3.3 further explain the two kinds of nonconformances. In the case of AQL level above 100, you are talking about nonconformities per 100 units. You may find more than 1 defect in 1 sample so the total number of defects may exceed the number of samples.
Hi. Thank you for the informative outline. From having read various articles explaining AQL, it appears to be a simple % value that the customer is willing to accept. eg. 2.5 is an indication that the customer is willing to accept 2.5% rejects in his batch. If this is the case, what do the AQL values above 100 mean? Have I misunderstood something? Please explain what AQL levels above 100 indicate
I absolutely adore reading your blog posts, the variety of writing is smashing.This blog as usual was educational, I have had to bookmark your site and subscribe to your feed in ifeed. Your theme looks lovely.Thanks for sharing.
Regards
iso 9000
Thanks a lot for the nice comment! We’ll try to keep up the nice work.
I absolutely adore reading your blog posts, the variety of writing is smashing.This blog as usual was educational, I have had to bookmark your site and subscribe to your feed in ifeed. Your theme looks lovely.Thanks for sharing.
Regards
iso 9000
Thanks a lot for the nice comment! We’ll try to keep up the nice work.